Our Health Library information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Please be advised that this information is made available to assist our patients to learn more about their health. Our providers may not see and/or treat all topics found herein.
Cuts
Overview
Cuts are open wounds through the skin. Normally the skin is under slight, constant tension as it covers the body. A cut is a forceful injury to the skin. Many people cut themselves by accident with household items, work items, or yard tools or when operating machinery. Children often are cut during play and sports activities or from falls while riding wheeled toys, such as bikes, scooters, or skateboards. Most cuts are minor, and home treatment is usually all that is needed.
Types of cuts
Some types of cuts are more serious and need to be checked and treated by a doctor. These more serious cuts include:
- Long or deep cuts.
- Cuts that open with movement of the body area, such as a cut over a joint. A cut over a joint may take a long time to heal because of the movement of the wound's edges.
- Cuts that may scar and affect the way a part of the body looks or functions. A cut on an eyelid or lip that doesn't heal well may cause problems with function or leave a noticeable scar.
- Cuts that remove all of the layers of the skin (avulsion injuries), such as slicing off the tip of a finger. An avulsion injury may take a long time to heal.
- Cuts from an animal or human bite. Infection is more likely with a bite injury.
- Cuts that have damage to tissues under the cut. Injuries to nerves, tendons, or joints are more common with cuts on the hands or feet. Slight swelling, bruising, and tenderness around a cut, bite, scrape, or puncture wound is normal. Swelling or bruising that begins within 30 minutes after the injury often means there is a large amount of bleeding or that deeper tissues are damaged.
- Cuts over a possible broken bone. Bacteria can get into a cut over a broken bone and infect the bone.
- Cuts caused by a crushing injury. With this type of injury, the cut may have occurred when the skin split open from the force of the injury. The force of the injury may also damage tissues and blood vessels under the cut. Crush injuries have a high risk of infection.
- Cuts that have or are thought to have an object still in the wound. For example, the object might be glass or wood.
Injury to the skin may also break small blood vessels under the skin. This can cause more swelling and bruising than you would expect.
Check Your Symptoms
The medical assessment of symptoms is based on the body parts you have.
- If you are transgender or nonbinary, choose the sex that matches the body parts (such as ovaries, testes, prostate, breasts, penis, or vagina) you now have in the area where you are having symptoms.
- If your symptoms aren’t related to those organs, you can choose the gender you identify with.
- If you have some organs of both sexes, you may need to go through this triage tool twice (once as "male" and once as "female"). This will make sure that the tool asks the right questions for you.
Many things can affect how your body responds to a symptom and what kind of care you may need. These include:
- Your age. Babies and older adults tend to get sicker quicker.
- Your overall health. If you have a condition such as diabetes, HIV, cancer, or heart disease, you may need to pay closer attention to certain symptoms and seek care sooner.
- Medicines you take. Certain medicines, such as blood thinners (anticoagulants), medicines that suppress the immune system like steroids or chemotherapy, herbal remedies, or supplements can cause symptoms or make them worse.
- Recent health events, such as surgery or injury. These kinds of events can cause symptoms afterwards or make them more serious.
- Your health habits and lifestyle, such as eating and exercise habits, smoking, alcohol or drug use, sexual history, and travel.
Try Home Treatment
You have answered all the questions. Based on your answers, you may be able to take care of this problem at home.
- Try home treatment to relieve the symptoms.
- Call your doctor if symptoms get worse or you have any concerns (for example, if symptoms are not getting better as you would expect). You may need care sooner.
Symptoms of infection may include:
- Increased pain, swelling, warmth, or redness in or around the area.
- Red streaks leading from the area.
- Pus draining from the area.
- A fever.
To clean a wound well:
- Wash your hands first.
- Remove large pieces of dirt or debris from the wound with cleaned tweezers. Do not push the tweezers deeply into the wound.
- Hold the wound under cool running water. If you have a sprayer in your sink, you can use it to help remove dirt and other debris from the wound.
- Scrub gently with water, a mild soap, and a washcloth.
- If some dirt or other debris is still in the wound, clean it again.
- If the wound starts to bleed, put direct, steady pressure on it.
If a chemical has caused a wound or burn, follow the instructions on the chemical's container or call Poison Control (1-800-222-1222) to find out what to do. Most chemicals should be rinsed off with lots of water, but with some chemicals, water may make the burn worse.
Certain health conditions and medicines weaken the immune system's ability to fight off infection and illness. Some examples in adults are:
- Diseases such as diabetes, cancer, heart disease, and HIV/AIDS.
- Long-term alcohol and drug problems.
- Steroid medicines, which may be used to treat a variety of conditions.
- Chemotherapy and radiation therapy for cancer.
- Other medicines used to treat autoimmune disease.
- Medicines taken after organ transplant.
- Not having a spleen.
Usually found in dirt and soil, tetanus bacteria typically enter the body through a wound. Wounds may include a bite, a cut, a puncture, a burn, a scrape, insect bites, or any injury that may cause broken skin. Tetanus can also happen with other infections, like dental infections. It can happen during a surgery or pregnancy and delivery.
A wound can be so small, you may not notice you have one. Or a skin blister could break and become an open wound. If there is any delay in finding or cleaning a wound, there is an increased risk for skin infection and a chance for tetanus to get in the wound. A tetanus infection can start 3 to 21 days after the bacteria enter the wound. Be especially careful about wounds on your fingers and toes.
Many people may not know when they got their last tetanus shot. So it's a good idea to call your doctor to see if you need one.
Make sure to stay up to date on your tetanus shots. A tetanus shot is recommended:
- For a dirty wound that has things like dirt, saliva, or feces in it, if you haven't had a tetanus shot in the past 5 years.
- For a clean wound, if you haven't had a tetanus shot in the past 10 years.
Pain in adults and older children
- Severe pain (8 to 10): The pain is so bad that you can't stand it for more than a few hours, can't sleep, and can't do anything else except focus on the pain.
- Moderate pain (5 to 7): The pain is bad enough to disrupt your normal activities and your sleep, but you can tolerate it for hours or days. Moderate can also mean pain that comes and goes even if it's severe when it's there.
- Mild pain (1 to 4): You notice the pain, but it is not bad enough to disrupt your sleep or activities.
Pain in children under 3 years
It can be hard to tell how much pain a baby or toddler is in.
- Severe pain (8 to 10): The pain is so bad that the baby cannot sleep, cannot get comfortable, and cries constantly no matter what you do. The baby may kick, make fists, or grimace.
- Moderate pain (5 to 7): The baby is very fussy, clings to you a lot, and may have trouble sleeping but responds when you try to comfort him or her.
- Mild pain (1 to 4): The baby is a little fussy and clings to you a little but responds when you try to comfort him or her.
Some types of facial wounds are more likely to leave a scar than others. These include:
- Jagged wounds on the face.
- Cuts on the eyelids.
- Cuts to the lips, especially if they cut through the edge of the lip.
Stitches or other treatment may help prevent scarring. It's best to get treated within 8 hours of the injury.
With severe bleeding, any of these may be true:
- Blood is pumping from the wound.
- The bleeding does not stop or slow down with pressure.
- Blood is quickly soaking through bandage after bandage.
With moderate bleeding, any of these may be true:
- The bleeding slows or stops with pressure but starts again if you remove the pressure.
- The blood may soak through a few bandages, but it is not fast or out of control.
With mild bleeding, any of these may be true:
- The bleeding stops on its own or with pressure.
- The bleeding stops or slows to an ooze or trickle after 15 minutes of pressure. It may ooze or trickle for up to 45 minutes.
Symptoms of difficulty breathing can range from mild to severe. For example:
- You may feel a little out of breath but still be able to talk (mild difficulty breathing), or you may be so out of breath that you cannot talk at all (severe difficulty breathing).
- It may be getting hard to breathe with activity (mild difficulty breathing), or you may have to work very hard to breathe even when you're at rest (severe difficulty breathing).
Seek Care Now
Based on your answers, you may need care right away. The problem is likely to get worse without medical care.
- Call your doctor now to discuss the symptoms and arrange for care.
- If you cannot reach your doctor or you don't have one, seek care in the next hour.
- You do not need to call an ambulance unless:
- You cannot travel safely either by driving yourself or by having someone else drive you.
- You are in an area where heavy traffic or other problems may slow you down.
Seek Care Today
Based on your answers, you may need care soon. The problem probably will not get better without medical care.
- Call your doctor or telehealth provider today to discuss the symptoms and arrange for care.
- If you cannot reach your doctor or telehealth provider or you don't have one, seek care today.
- If it is evening, watch the symptoms and seek care in the morning.
- If the symptoms get worse, seek care sooner.
What are your options for medical care?
Today your options for where to get your medical care are greater than ever before. You may not even have to leave your home to get the care you want and need. You can choose based on what your health problem is and what works best for you.
- Telehealth is a video call with a health care provider. It can be a convenient way to get medical advice or treatment. Some insurers provide access to telehealth that may be available 24 hours a day. Telehealth for less serious problems may cost less and be faster than in-person clinic visits.
- Urgent care and retail clinics are options if you don't have a doctor, you can't or don't want to wait to see your own doctor, or a telehealth visit can’t treat the problem.
- Virtual care from your primary provider or a telehealth service can be delivered through your smartphone, computer, or tablet.
Call 911 Now
Based on your answers, you need emergency care.
Call 911 or other emergency services now.
Sometimes people don't want to call 911. They may think that their symptoms aren't serious or that they can just get someone else to drive them. Or they might be concerned about the cost. But based on your answers, the safest and quickest way for you to get the care you need is to call 911 for medical transport to the hospital.
Call 911 Now
Based on your answers, you need emergency care.
Call 911 or other emergency services now.
Put direct, steady pressure on the wound until help arrives. Keep the area raised if you can.
Sometimes people don't want to call 911. They may think that their symptoms aren't serious or that they can just get someone else to drive them. Or they might be concerned about the cost. But based on your answers, the safest and quickest way for you to get the care you need is to call 911 for medical transport to the hospital.
Self-Care
Minor cuts usually can be treated at home. Home treatment can help prevent infection and promote healing.
Try these tips for treating a cut.
- Stop the bleeding.
Apply direct pressure to the wound.
Nonprescription products can be applied to the skin to help stop mild bleeding of minor cuts, lacerations, or scrapes. Before you buy or use these products, be sure to read the label carefully. Follow the label's instructions when you apply the product.
Cuts to the head or face may look worse than they are and may bleed a lot because of the good blood supply to these areas. Controlling the bleeding will help you see how serious the injury is.
- Clean the wound as soon as you can.
This lowers the chance of infection, scarring, and tattooing of the skin from dirt left in the wound. (If dirt or other debris is not removed from a cut, the new skin will heal over it. The dirt can then be seen through the skin and may look like a tattoo.)
- Use cleaned tweezers to remove large pieces of dirt or other debris from the wound. Don't push the tweezers deeply into the wound.
- Wash the wound for 5 minutes with large amounts of cool, clean water. Some nonprescription products for wound cleaning can numb the area so that cleaning doesn't hurt as much. Be sure to read the product label for correct use.
- Don't use rubbing alcohol, hydrogen peroxide, iodine, or Mercurochrome. They can harm the tissue and slow healing.
- Check to see if other tissues have been injured.
These tissues include blood vessels, nerves, tendons, ligaments, joints, bones, and internal organs.
- Apply a bandage, if needed.
Most cuts heal well and may not need a bandage. You may need to protect the cut from dirt or irritation. Be sure to clean the cut thoroughly before bandaging it. Cleaning reduces the chance that you'll get an infection under the bandage.
If you use a bandage:
- Choose the bandage carefully. There are many products available. Liquid skin bandages and moisture-enhancing bandages are available with other first aid products. Before you buy or use one, be sure to read the label carefully. Follow the label's instructions when you put on the bandage.
- If you use a cloth-like bandage, apply a clean bandage when it gets wet or soiled. This will also help prevent infection. If a bandage is stuck to a scab, soak it in warm water. Soaking it will soften the scab and make the bandage easier to remove. If available, use a nonstick dressing. There are many bandage products available. Be sure to read the product label for correct use.
- Watch for signs of infection. If you have an infection under a bandage, you may need treatment from a doctor.
- Apply a thin layer of petroleum jelly, such as Vaseline, lightly to the wound. It will keep the bandage from sticking to the wound.
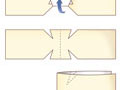
- Use an adhesive strip to hold the edges of a wound together. Always put an adhesive strip across a wound to hold the edges together, not lengthwise. You can make a butterfly bandage at home or buy one to help hold the skin edges together.
- Treat pain and swelling.
Prop up the injured area on a pillow anytime you sit or lie down. Try to keep the area at or above the level of your heart to reduce swelling.
If you are concerned that the injury is more serious, you may need to be checked by a doctor to see if you need stitches or a tetanus shot.
Need for stitches
To determine whether you need stitches, stop the bleeding and wash the wound well. Then pinch the sides of the wound together. If the wound's edges come together and it looks better, you may need stitches. If stitches may be needed, avoid using antiseptic until after a doctor checks the wound.
- Most cuts that need treatment should be stitched, stapled, or closed with skin adhesive within 6 to 8 hours after the injury.
- Some cuts that need treatment can be closed up to 24 hours after the injury. Your risk of infection increases the longer the cut stays open.
- Sometimes a wound with a high risk of infection won't be stitched until after 24 hours, or won't be stitched at all, so it can be cleaned well to prevent infection.
- A cut from a clean object may be stitched 12 to 24 hours after the injury depending on the location of the cut.
Need for a tetanus shot
To decide if you need a tetanus shot after a wound, first decide if the object that caused the wound was dirty or clean. An object is dirty if it has dirt, soil, spit, or feces on it. A clean object does not have dirt, soil, spit, or feces on it.
You will need a tetanus shot if:
- Your wound was caused by something that was clean and your last tetanus shot was longer than 10 years ago.
- Your wound was caused by something that was dirty and your last tetanus shot was longer than 5 years ago.
- You are not sure if your wound was caused by something clean or dirty and your last tetanus shot was longer than 5 years ago.
- You are not sure when you had your last tetanus shot.
- You did not get the first series of tetanus shots (primary vaccination series).
If you need a tetanus shot, call your doctor to arrange for a shot.
Some people may need tetanus immunoglobulin (IG) for a wound that is at high risk for developing tetanus. The immunoglobulin is usually only needed if you have not (or do not know if you have) completed the tetanus primary vaccination series.
When to call for help during self-care
Call a doctor if any of the following occur during self-care at home:
- New or worse signs of infection, such as redness, warmth, swelling, pus, or a fever.
- New loss of function near the wound.
- Decreased blood flow, such as cool, pale skin near the wound.
- Pain gets worse.
- Symptoms occur more often or are more severe.
Learn more
Over-the-counter medicines
- Acetaminophen
- Aspirin for Pain, Fever, and Inflammation
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Quick Tips: Safely Giving Over-the-Counter Medicines to Children
More self-care
Preparing For Your Appointment
You can help your doctor diagnose and treat your condition by being prepared for your appointment.
Related Information
Credits
Current as of: July 31, 2024
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
Current as of: July 31, 2024
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Ignite Healthwise, LLC disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. Learn how we develop our content.
To learn more about Ignite Healthwise, LLC, visit webmdignite.com.
© 2024-2025 Ignite Healthwise, LLC.